Marsico Hall Microscopes Facility (MHMF.ORG)
|
|
Marsico Hall Microscopes Facility (MHMF.ORG) |
Background Correction of unevenness of illumination
in transmitted light images
Background ratioing is a technique which compensates for the inevitable unevenness in transmitted light photo micrographs. Unevenness is inherent with Kohler illumination, even with the condenser focus and centering fully optimized and the condenser aperture fully opened. These settings give the flattest (most even) field of illumination. With transmitted light images unevenness of illumination causes images acquired by camera to have darker edges (vignetting). When viewing down the microscope eye pieces the eye is forgiving of these darker edges. However the camera records them clearly, especially when contrast enhancement is applied.
Simple image processing can reduce shading. An image of the field of view of interest, can be flattened by taking a background image of a blank region of the sample under identical conditions. When taking an image of a blank region on the slide dirt, dust, etc. can be removed by defocusing. Either the background image can be subtracted from the sample image (good for fluorescence), or better still, the sample image can be divided by the background image. In both cases the intensity should be rescaled. C-Imaging steps to carry out shading correction are given here.
An example of background (shading) correction:
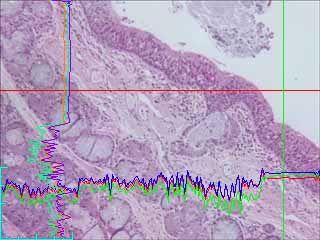
Transmitted light image of an H&E stain lung section. Note the darker band at the left edge, and, to a lesser extent, on the right edge. [image 1]
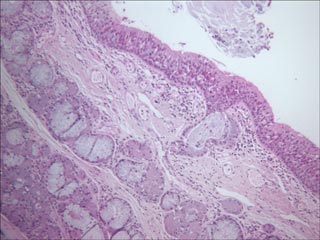
The dark bands are clearly shown in the line histograms take at the vertical straight line and horizontal strait red lines. The horizontal intensity shows a curvature down on the right, and the left edge has less intensity than the central region, even though the section has no structure that ought to be darker at that edge.
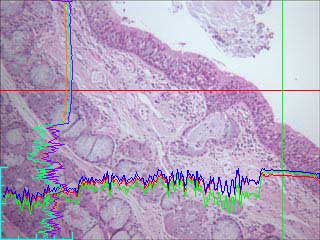
Blank region of slide showing shading (darker on the left and right edges) [image 2]. The microscope has been setup for optimum Kohler illumination, including opening the condenser aperture to its maximum.

Line histograms of vertical (green) and horizontal (red) cross hairs show curvature due to shading as a result of the unevenness of the illumination.
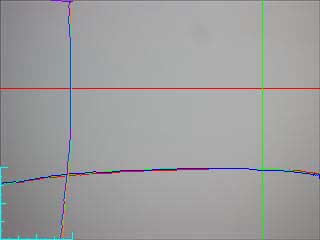
Image 1 ratioed with image 2 and scaled using the "enhance", "process" and "ratio shade correction" feature of SimplePCI. Similar processing can be done in Photoshop and many other image processing programs.
After shading correction the red cross hair line histograms now does not have the curve down on the right hand edge or the lower levels on the left hand edge. Also the non noisy region of the vertical line histogram (of the green line) is straight.
C-Imaging steps to carry out shading correction are given here
Factors to consider:
|
|
|
Copyright 2001-2025 Dr. M. Chua, School of Medicine, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC 27599 |
| Go Back | Booking Resources |
Questions/comments/problems: Michael Chua |
|
|
Last Updated: 2026-01-01 |